How the ratchet mechanism works
Ratchet and pawl, a one-way intermittent motion Ratchet Straps mechanism composed of ratchets and pawls. The ratchet mechanism is commonly used in various machine tools and automatic machines for intermittent feed or rotary table indexing, and it is also commonly used on jacks. The ratchet mechanism is used for one-way drive in bicycles, and the ratchet mechanism is commonly used in manual winches to prevent reverse rotation. The ratchet mechanism is often accompanied by noise and vibration when it works, so its working frequency cannot be too high. The ratchet gear usually uses one-way teeth. The pawl is hinged on the rocker.
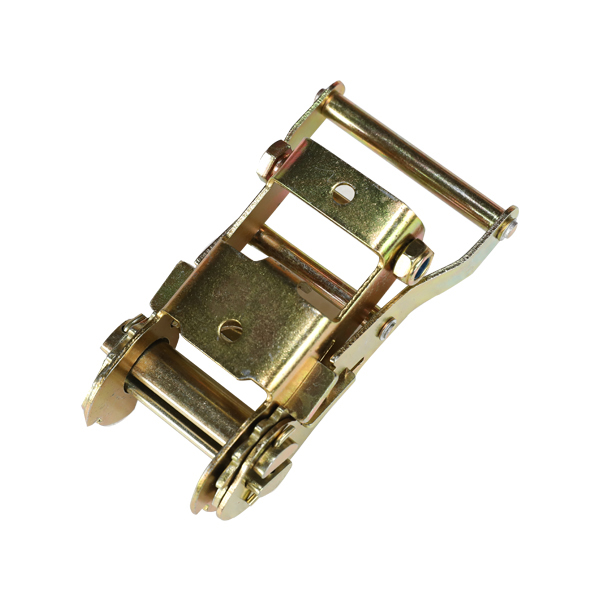

When the rocker swings counterclockwise, the drive pawl is inserted into the ratchet teeth to push the ratchet to rotate in the same direction; when the rocker swings clockwise, the ratchet The paw slides over the ratchet, and the ratchet stops rotating. In order to ensure that the ratchet does not reverse, a non-reversal pawl is often installed on the fixed member. The reciprocating swing of the rocker can be realized by a crank rocker mechanism, a gear mechanism and a swing cylinder which transmits little power.It is composed of active swing rod, pawl, ratchet, non-return pawl and frame. The driving part is hollowed on the driven shaft fixedly connected with the ratchet wheel, and is connected with the rotating pair of the driving pawl. When the driving member swings in the counterclockwise direction, the driving pawl is inserted into the tooth groove of the ratchet wheel, and the ratchet wheel is rotated through a certain angle.
At this time, the non-return pawl slides on the tooth back of the ratchet wheel. When the driving member rotates in the clockwise direction, the non-return pawl prevents the ratchet from rotating in the clockwise direction, while the driving pawl can slide on the back of the ratchet tooth, so the ratchet is stationary at this time. Therefore, when the driving member makes continuous reciprocating swing, the ratchet makes a one-way intermittent movement. When using an electromagnet to directly drive the pawl. The angle the ratchet rotates each time is called the stroke. The size of the stroke can be adjusted by changing the structural parameters of the drive mechanism or the position of the gear cover, or it can be adjusted during operation.
If the adjustment accuracy is desired to be higher than the angle corresponding to a ratchet, a multi-pawl ratchet mechanism can be used. The toothed ratchet mechanism has a simple structure and is convenient to manufacture; the time ratio between movement and stop can be achieved by selecting a suitable drive mechanism. The disadvantage of this mechanism is that the stroke can only be adjusted in stages; the noise, impact and wear are large, so it is not suitable for high speed. The friction type ratchet mechanism uses an eccentric sector wedge to replace the pawl in the tooth type ratchet mechanism, and replaces the ratchet wheel with toothless friction. It is characterized by smooth transmission and no noise; the stroke can be steplessly adjusted. However, due to frictional transmission, slipping will occur. Although it can play a safety protection role, the transmission accuracy is not high. Suitable for occasions with low speed and light load.
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch